Exit plan: Five steps to quit pesticides crop by crop
- Pesticides
The biodiversity crisis is getting worse rapidly. Pesticides, a major factor in agricultural intensification, play a significant role. foodwatch proposes a five steps crop-by-crop approach to reduce pesticide use.
According to the European Environment Agency, "agricultural intensification is one of the main causes of biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation in Europe." Despite this, efforts to reduce pesticide use haven't worked well. The EU has used more pesticides since the 1990s, and the European Commission has dropped its goal to cut the use of chemical pesticides, especially the most dangerous ones, by half.
It is clear that we have to act now. New approaches to stop the use of pesticides are urgently needed in order to curb their negative impacts on human health, the environment and biodiversity.
The five-step phase-out plan follows an innovative crop-by-crop approach, starting with crops like cereals and maize where pesticide use is most widespread, but removing them from the process is the easiest and cheapest. This step-by-step procedure will help to effectively reduce the amount of pesticides used without compromising agricultural productivity.
The loss of biodiversity and the degradation of ecosystems are continuing at an alarming rate. We have to act now to protect the food system and the environment – without threatening the livelihood of farmers. Our five-step-plan is not an NGO fairytale but a realistic approach to make agriculture more sustainable.Campaigner
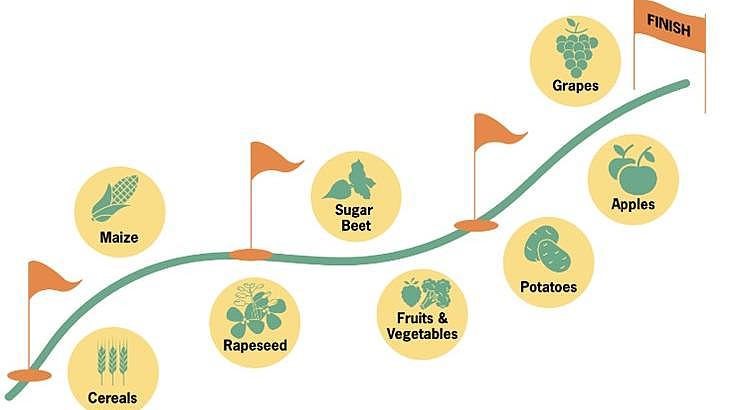
The five steps to a pesticide exit:
- Look at individual crops: An exit must start with crops where pesticide reduction is the easiest. Proceeding crop-by-crop instead of a full pesticide exit at once will make reduction feasible and effective.
- Start with the easiest and largest crop: Fortunately, many of the crops currently cultivated in Europe have the potential for pesticide-free production with relatively simple agronomic adjustments, like crop rotation and tillage, at little extra cost. This includes crops like cereals and maize, which constitute a significant proportion of EU agricultural area. Cereals stand out as significant consumers of pesticides within the European Union. For instance, in Germany, wheat and barley alone contribute to 45% of pesticide usage.
- Implement specific measures: Besides agricultural methods tailored to each crop, such as optimising crop rotation, promoting natural pest predators, and adopting resistant varieties, pesticide use can be significantly reduced by political measures: firstly, an EU-wide introduction of a tax on pesticide sales, graded according to toxicity and efficacy. Secondly, a reform of the current pesticide authorisation practice. Currently, the authorisation of every third pesticide in the EU has long since expired, yet the products are still sprayed on a massive scale. All authorisations for pesticides must be reviewed for their absolute necessity.
- Making pesticide-free cereals the new standard: An examination of retailers in Germany, France, and the Netherlands indicates that they often lack a comprehensive strategy for reducing and phasing out pesticides in cereal production. Retailers must step forward to make their entire range of cereal and grain products pesticide-free, implement a procurement policy for “pesticide-free” grain products, and ensure transparency throughout the process by publishing annual data on pesticide use.
- Get inspired by positive examples: Pesticide-free cereal production is already happening in Europe. Retailer Migros in Switzerland promotes pesticide-free production with various projects in collaboration with a union of Swiss produce farmers. Another example of pesticide-free bread is the bakery Maurer, located in Germany, which has established itself as a pioneer in promoting sustainable and pesticide-free agricultural practices. The bakery sources grain from over 900,000 square metres of arable land in the Rems-Murr district without pesticides, genetic engineering, or growth regulators.
The foodwatch report “The Dark side of Grains” published end of last year showed that one third of cereal grain products in Europe are contaminated with pesticide residues. The data from the European Safety Authority showed great variety in the prevalence of pesticide residues, ranging from less than 10 percent in samples of emmer grain and rye to nearly 90 percent in wheat bread and rolls.
